The watery eye capsule
✍ common complaint, particularly in the elderly population.
✍ ranges from the transient and trivial (associated with a local irritant) to the permanent and disabling.
✅ ur stepwise approach for watery eye
✍ symptoms
• episodic/permanent
• frequency of wiping eyes
• exacerbating factors (in/outside, cold/warm)
• site where tears spill over (laterally/medially)
✍ History
• previous surgery/trauma
• concurrent eye disease(HSV)
• previous ENT problems (sinusitis, surgery/nasal fracture, granulomatous disease)
• pro-secretory drugs (pilocarpine)
• Allergies or relevant drug contraindications
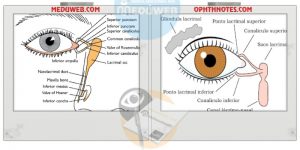
✅ examination of watery eye
✍ VA
• Best corrected/pinhole
✍ face
• Scars (previous trauma/surgery)
• asymmetry
• prominent nasal bridge
• mid-face hypoplasia
• age-related sag
✍Lacrimal sac
• Swelling
• any punctal regurgitation on palpation
✍ Lid
• MGD disease
• lash malposition
• lid position (ectropion,entropion,or low lateral canthus)
• laxity (lid and canthal tendons)
✍ punctum
• position
• scarring
• concretions
• patency
✍ conjunctiva
• Irritation (chronic conjunctivitis)
• Inflammation
✍ cornea
• chronic corneal disease
✍ tear film
• meniscus high/low
• TBUT
• dry eye (Schirmer’s test)
✍ Fluorescein dye disappearance test (FDT)
• tear film height
• symmetry
• dilution
✍ Dye recovery
• Jones I (physiological—without syringing)
• Jones II (non-physiological—after syringing)
• retrieve dye with cotton bud under inferior turbinate or ideally visualize with nasendoscope
✍ canulation
• patency of puncta
✍ syringing
• Do gently with lateral distraction of lid to avoid false passage
• do not advance through an obstruction
• Careful assessment will indicate site of obstruction
• assess flow and regurgitation through upper or lower punctum, and presence of fluoresceine or mucous in the fluid
• perform nasendoscopy where possible
• CT DCG if previous trauma/destructive disease/suspected tumour.
• Lacrimal scintigraphy is more useful than DCG as it simulates physiologic tear drainage conditions.
most common causes of watery eye
✅ Increased production
✍Autonomic disturbance
✍ pro-secretory drugs
✍ Chronic lid disease (blepharitis)
✍ Local irritant (FB, trichiasis)
✍ Systemic disease (TED)
✍ Chronic conjunctival disease (OMMP)
✍ Chronic corneal disease (KCS)
✅ Lacrimal pump failure
✍ Lid laxity
✍ Orbicularis weakness (VIIn palsy)
✍ Lid position Entropion or Ectropion
✅ Decreased drainage
✍ punctal obstruction
Congenital
* punctal atresia
* accessory punctum
Idiopathic stenosis (elderly) 2° to punctal eversion
HSV infection
post-irradiation
Trachoma
Cicatricial conjunctivitis
✍ Canalicular obstruction
Idiopathic fibrosis
HSV infection
Actinomyces
Chronic dacrocystitis
Cicatricial conjunctivitis
5-FU administration (systemic)
✍ Lacrimal sac obstruction
granuloma,
sarcoid
syphilis
fungi
papillomas
epithelial papillary (squamous and transitional cell) carcinomas
Lymphoma
Invasive pharyngeal or sinus carcinoma
✍ nasolacrimal duct obstruction
Congenital(delayed canalization)
Idiopathic stenosis
Trauma (nasal or orbital fracture)
nasal pathology (chronic inflammatory polyps)
post-irradiation
granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)
Tumours (nasopharyngeal carcinoma)
never to forget the most important DD of watery eye
✍ in children ( glaucoma)
✍ in adults ( Sebaceous gland carcinoma may resemble chronic conjunctivitis)
The watery eye videos:
Tearing (Watery eyes) – YouTube
The watery eye PowerPoint presentations :
Watery eye
The watery eye capsule


