Management of Rh Negative Pregnant Women who Received Rh Positive Blood OR who are Sensitized by Rh Positive Fetal Blood:
– At first do ICT to check for sensitivity & if positive, do antibody titre.
– Ab titre is done monthly if stable result & every 2 wk if rising titre.
– If a critical level is reached (>16 or 32), do MCA-PSV Doppler at 1-2 wk intervals.
– MCA-PSV indicate the velocity of blood flow in the MCA which increases as fetal Hb
level falls (anemia) due to the fast blood flow in the MCA due to decreased viscosity.
– If MCA-PSV ≤1.5 MoM for gestational age, this indicate the absence of moderate to
severe anemia & if it remains at this level, we begin weekly antenatal surveillance at 32
wk (CTG, BPP, fetal movement count, AF volume & Doppler assessment), then we
schedule delivery at 37-38 wk.
– If MCA-PSV >1.5 MoM, transfere her to a fetal medicine center to obtain a fetal blood
for Hb checking & a possible intrauterine transfusion if Hct<30%. Then they consider
delivery at 35 wk.
– Fetal Hb/Hct should be checked before transfusion because a high MCA-PSV is not a
definitive proof of clinically significant fetal anemia; false positives occur.
– Intravascular intrauterine transfusion is generally limited to pregnancies between 18-35
wk because before 18 wk, the small size of the relevant anatomic structures poses
technical challenges, and after 35 wk, intrauterine transfusion is considered riskier than
delivery followed by postnatal transfusion therapy.
Abbreviations:
– ICT: indirect Coombs titer.
– MCA-PSV: middle cerebral artery (MCA) peak systolic velocity (PSV).
Rh incompatibility ( isoimmunization ) power point presentation :
1. Rh-ISOIMMUNIZATION DR.SURENDRA NATH BERA DR. MITALI DASH M K C G MEDICAL COLLEGE , ORISSA
2. ISOIMMUNIZATION: A process by which immune antibodies are produced in a person by the entry of an antigen of another individual of same species, the former lacking the antigen.
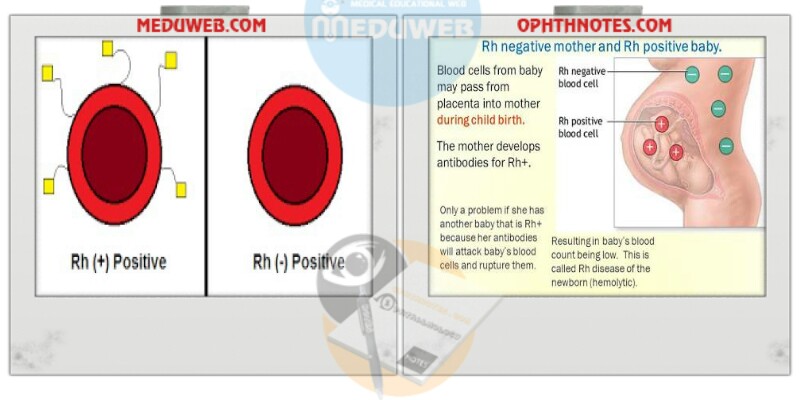
3. Rh- Iso imunization Definition known as: Rhesus incompatibility ,Rhesus disease RhD Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn. -When Rh– mother gets pregnant to Rh+ fetus —she may be sensitized to Rh antigen and develop antibodies. These will cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal red blood cells.
4. HISTORY 1609-description of hydrops fetalis. 1939-Levine and Stetson discovered atypical aglutinin. 1940-Landsteiner and wiener Rh-antigen. 1941-Levine discover Rh-antidody.
5. Rhesus factor (1940): Agglutinogen (C,D,E) – mainly D C,D,E – dominant antigen c,e – recessive antigen Person lack D-antigen called Rh-ve
6. – Rh positive (85%) – homozygous (DD) (35%), or heterozygous (Dd) (50%) – Rh negative (15%) – Incidence of Rh-ve in far east is about 1% Examples of Rh factor: (CDe=R1) , (Cde=r) (cDE=R2) Other systems: Kell. Lweis, Deigo, luther, Duffy, MNS,
7. Kell is most common of minor gr. Responsible for 10% of cases of severe antibody-mediated anemia Only anti-Fy(a) antibody associated with HDFN- may range from mild to sever.
8. INCIDENCE OF Rh-ve Chinese and Japanese 1% North American Indian 1—2% Indo-Eurasian 2% india 5% African American 4 – 8% Caucasian 15 – 16% Basque 30 – 35%
Rh incompatibility videos: