Alarms of Retinal Detachment
• floaters
• flashes of light (photopsia) in the dark
Symptoms of Retinal Detachment of Alarms of Retinal Detachment:
• shadow in front of the eye
• black rains
• swarm of bees
• cloud ☁️ or curtain from above
• wall from below

Signs of Retinal Detachment of Alarms of Retinal Detachment:
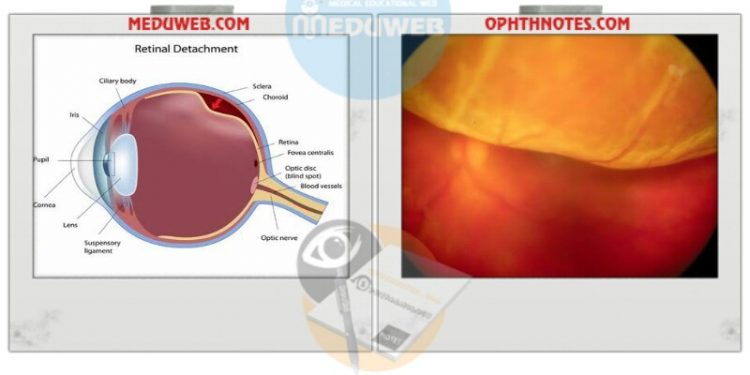
• detached retina is gray
• choroidal structure no longer visible
• pink shimmer of the choroid absent
• vessels have paintlike appearance
• reflex on arterioles absent
• fine wrinkles on the surface of the retina
• retinal blister floating back and forth
• retinal hole at the top of the blister
• visual field defect
• sharply dropped VA if macula is detached
• subretinal fibrosis and PVR with immobile retina ( in 3 months)
• intraretinal cyst ( within 1 yr)
Alarms of Retinal Detachment PowerPoint presentation:
Retinal detachment
- DR DINESH MITTAL DR SONALEE MITTAL DRISHTI EYE HOSP VIJAYNAGAR INDORE
- RETINAL DETACHMENT • retinal detachment is used to describe a separation of the neurosensory retina from retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). • A retinal detachment re-establishes the potential space that exists between the original layers of the embryonic optic cup.
- TYPES OF RD • Three categories of RD are rhegmatogenous, exudative, and tractional. • Rhegmatogenous RD are sometimes referred to as primary detachments, while both exudative and tractional detachments are called secondary or nonrhegmatogenous detachments .
- RHEGMATOGENOUS RD •Rhegmatogenous detachments are the most common form of retinal detachment. They are caused by a break in the retina through which fluid passes from vitreous cavity into subretinal space. • The responsible break(s) can be identified preoperatively in more than 90%of cases, but occasionally presence of a minute, unseen break must be assumed.
- EXUDATIVE RD •Exudative detachments, also called serous detachments, are due to an associated problem that produces subretinal fluid without a retinal break. This underlying problem usually involves the choroid as a tumor or an inflammatory disorder.
- TRACTIONAL RD •Tractional detachments occur when pathologic vitreoretinal adhesions or membranes mechanically pull the retina away from the pigment epithelium without a retinal break. The most common causes include PDR , ROP , proliferative sickle retinopathy, and penetrating trauma. •Retinal breaks may subsequently develop, resulting in a combined tractional and rhegmatogenous detachment.
- MECHANISM OF RHEGMATOGENOUS RD • requirements for a rhegmatogenous RD include a retinal break and low-viscosity vitreous passing through break into the subretinal space. The usual sequence causing retinal detachment is vitreous liquefaction followed by a PVD that causes traction at site of significant vitreoretinal adhesion with a subsequent retinal tear. Fluids from vitreous cavity then pass through tear into subretinal space .
Alarms of Retinal Detachment Videos:
Retinal Detachment | Signs, Symptoms and Treatment video
Alarms of Retinal Detachment